Exercises
Tick the most suitable answer in questions 1 and 2.
1. In addition to the rock particles, the soil contains
(i) air and water
(ii) water and plants
(iii) minerals, organic matter, air and water
(iv) water, air and plants
Answer. (iii) minerals, organic matter, air and water
2. The water holding capacity is the highest in
(i) sandy soil
(ii) clayey soil
(iii) loamy soil
(iv) mixture of sand and loam
Answer. (ii) clayey soil
3. Match the items in Column I with those in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) A home for living organisms | (a) Large particles |
| (ii) Upper layer of the soil | (b) All kinds of soil |
| (iii) Sandy soil | (c) Dark in colour |
| (iv) Middle layer of the soil | (d) Small particles and packed tight |
| (v) Clayey soil | (e) Lesser amount of humus |
Answer.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) A home for living organisms | (b) All kinds of soil |
| (ii) Upper layer of the soil | (c) Dark in colour |
| (iii) Sandy soil | (a) Large particles |
| (iv) Middle layer of the soil | (e) Lesser amount of humus |
| (v) Clayey soil | (d) Small particles and packed tight |
4. Explain how soil is formed.
Answer. The soil is formed by the process of weathering in which the rocks break down by the action of wind, water and climate. It is a very slow process and big rocks get converted into soil.
5. How is clayey soil useful for crops?
Answer. Clayey soil is very useful for crops because it is rich in humus and are very fertile, so it is suitable for growing cereals like wheat and gram. Such soil is good at retaining water. For paddy, soils rich in clay and organic matter and having a good capacity to retain water are ideal. For lentils (masoor) and other pulses, loamy soils, which drain water easily, are required.
6. List the differences between clayey soil and sandy soil.
Answer.
| Clayey Soil | Loamy Soil |
| (i) It has much smaller particles. | (i) It has much larger particles. |
| (ii) It can hold good amount of water. | (ii) It cannot hold water. |
| (iii) It is fertile. | (iii) It is not fertile. |
| (iv) Air content is low. | (iv) Air get trapped between the particles. |
| (iv) Particles are tightly packed | (iv) Particles are loosely packed |
| (iv) Good for growing various crops. | (iv) Not suitable for growing crops. |
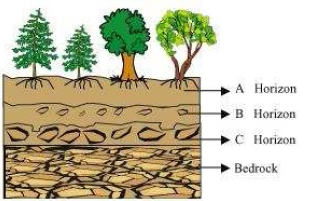
7. Sketch the cross section of soil and label the various layers.
Answer.
8. Razia conducted an experiment in the field related to the rate of percolation. She observed that it took 40 min for 200 mL of water to percolate through the soil sample. Calculate the rate of percolation.
Answer.
Amount of water taken = 200 mL
Time taken by water to percolate = 40 min
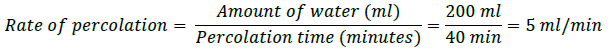
9. Explain how soil pollution and soil erosion could be prevented.
Answer. Steps for preventing soil pollution and soil erosion:
(i) Plantation should be encouraged because plant roots firmly bind the soil and help in preventing erosion.
(ii) Methods like crop rotation and mixed farming should be followed.
(iii) Use of organic fertilizers and manure instead of synthetic.
(iv) Pesticides and insecticides should be used in limited quantity and find natural way to prevent it.
(v) Plastic bags should b banned and it doesn’t decompose and gives rise to soil pollution.
(vi) Industrial waste shouldn’t be dumped directly as it kill necessary micro organisms of soil.
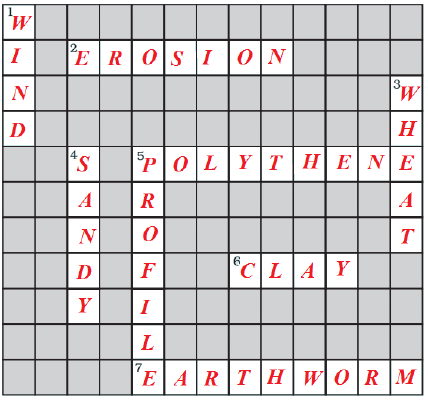
10. Solve the following crossword puzzle with the clues given:
Across
2. Plantation prevents it.
5. Use should be banned to avoid soil pollution.
6. Type of soil used for making pottery.
7. Living organism in the soil.
Down
1. In desert soil erosion occurs through.
3. Clay and loam are suitable for cereals like.
4. This type of soil can hold very little water.
5. Collective name for layers of soil.
Answer.
Across
2. Plantation prevents it. → Erosion
5. Use should be banned to avoid soil pollution. → Polythene
6. Type of soil used for making pottery. → Clay
7. Living organism in the soil. → Earthworm
Down
1. In desert soil erosion occurs through. → Wind
3. Clay and loam are suitable for cereals like. → Wheat
4. This type of soil can hold very little water. → Sandy
5. Collective name for layers of soil. → Profile