Exercises
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called _____________.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called_____________.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as _____________.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as _____________.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of _____________, _____________ and _____________.
Answer
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called vegetative propagation.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called unisexual.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as pollination.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as fertilisation.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of wind, water and animals.
2. Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Answer. Different methods of asexual reproduction:
(i) Vegetative propagation: In this asexual reproduction, new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds of individual plant. Examples: Stem cutting cutting in champa, eye growth in potatoes, bud in case of bryophyllum etc.
(ii) Budding: The bud is a small projection which gradually grows and gets detached from the parent cell and
forms a new yeast cell. The new yeast cell grows, matures and produces more yeast cells. example: Yeast.
(iii) Fragmentation: In this mode of reproduction, the growth and multiplication is done by rapidly breaking down into two or more fragments. Each pieces grow into new individuals whenwater and nutrients are available. Example: Algae
(iv) Spore Formation: This reproduction is done by spores which under favourable condition germinates and develops into a new individual. Examples: Moss and ferns.
3. Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Answer. When two parents are involved in reproduction, the method is called sexual reproduction. The male and female gametes fuse during fertilization to produce zygote. The zygote subsequently develops into an embryo which further develops into a new individual.
4. State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Answer
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
| (i) One parent is involved. | (i) Two parents are involved. |
| (ii) New generation is identical or true copy of their parent. | (ii) New born are similar to their parents. |
| (iii) It doesn’t require the formation of gametes. | (iii) It requires the formation of gametes. |
| (iv) Special organs for reproduction are not required. | (iv) Special organs for reproduction are required. |
| (v) Examples: Potato, Jasmine, Rose, Yeast, Bryophyllum etc. | (v) Examples: Mangoes, coconut, Hibiscus etc. |
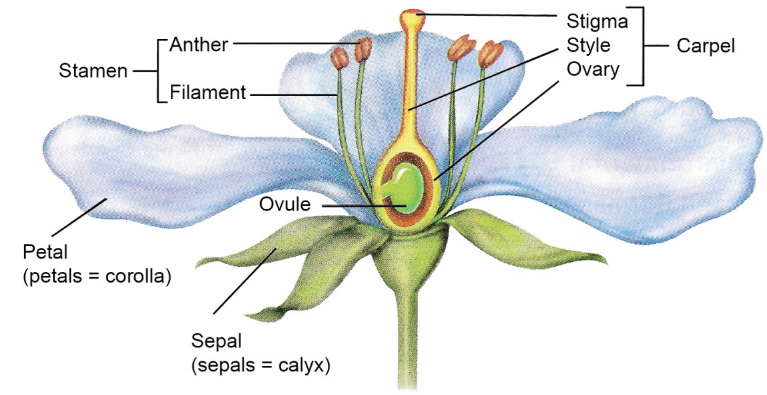
5. Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
Answer.
6. Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Answer.
| Self pollination | Cross Pollination |
| (i) Transfer of pollen from the stamen to the pistil of the same flower. | (i) Transfer of pollen from the stamen of one flower to the pistil of another flower of the same plant or different plants of the same kind. |
| (ii) External medium is not required. | (ii) External medium is required. |
| (iii) It occurs only in bisexual flower. | (iii) It occurs in both unisexual and bisexual flowers. |
7. How does the process of fertilisation take place in flowers?
Answer. Once pollen grain spreads on the stigma, it produces a pollen tube. This process is called germination of pollen grain. The pollen tube penetrates the style and reaches the ovary. Male nucleus is transferred through this pollen tube. Finally, fusion of male and female nuclei takes place inside the ovary. This step is called fertilization.
8. Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Answer. Various ways by which seeds are dispersed are:
(i) Dispersal by wind: Light seeds or hairy seeds and hairy fruit get blown off with the wind to far away places. Examples: Sunflower, maple, drumsticks etc.
(ii) Dispersal by water: Fruits or seeds which develop floating ability in the form of spongy or fibrous
outer coat are carried away with to different places. Example: Coconut.
(iii) Dispersal by animals or birds: Spiny seeds with hooks which get attached to the bodies of animals and
are carried to distant places. Also, the fruits are eaten up by animals and birds and their seeds get dispersed to far away places. Examples: Xanthium, Urena, Mango etc.
(iv) Dispersal by bursting: Some seeds are dispersed when the fruits burst with sudden jerks and the seeds
are scattered far from the parent plant. Examples: castor and balsam.
(v) Dispersal by human being: They also play an important role in seed dispersal especially during plantation and farming. They also transport fruits which also help in the dispersal of seeds.
9. Match items in Column I with those in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Bud | (i) Maple |
| (b) Eyes | (ii) Spirogyra |
| (c) Fragmentation | (iii) Yeast |
| (d) Wings | (iv) Bread mould |
| (e) Spores | (v) Potato |
| – | (vi) Rose |
Answer
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Bud | (iii) Yeast |
| (b) Eyes | (ii) Potato |
| (c) Fragmentation | (v) Spirogyra |
| (d) Wings | (i) Maple |
| (e) Spores | (iv) Bread mould |
10. Tick (✓) the correct answer:
(a) The reproductive part of a plant is the
(i) leaf (ii) stem (iii) root (iv) flower
Answer. (iv) flower
(b) The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called
(i) fertilisation (ii) pollination (iii) reproduction (iv) seed formation
Answer. (i) fertilisation
(c) Mature ovary forms the
(i) seed (ii) stamen (iii) pistil (iv) fruit
Answer. (iv) fruit
(d) A spore producing plant is
(i) rose (ii) bread mould (iii) potato (iv) ginger
Answer. (ii) bread mould
(e) Bryophyllum can reproduce by its
(i) stem (ii) leaves (iii) roots (iv) flower
Answer. (ii) leaves
